
Table of Contents
Introduction to Identity Lifecycle Management in IAM
Identity lifecycle management (ILM) refers to the process of managing user identities and access privileges throughout the entire lifecycle of an employee or other user within an organization. CyberArk defines ILM as “the creation, use, maintenance, and deletion of user accounts and their credentials as well as the management of user privileges throughout an account’s lifecycle”. Proper ILM ensures that users are granted appropriate access to systems and data based on their role and that access is reviewed and adjusted over time as needed. It is a critical component of an organization’s overall identity and access management (IAM).
ILM provides several significant benefits from a security and compliance perspective. By proactively managing identities and access, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches due to unauthorized access. It also helps enforce least privilege principles, meaning users are not granted unnecessary permissions beyond what they need to do their jobs. From an auditing standpoint, ILM can track user access and changes over time. Lastly, ILM helps organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements around access controls and user provisioning/de-provisioning. Given the alarming rise in data breaches and the expanding regulatory landscape, having strong ILM practices in place is becoming increasingly important for modern organizations.
Within the broader framework of IAM, ILM covers the entire user access lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding. It complements critical IAM capabilities like single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls. While those other components focus on authentication and authorization, ILM focuses on efficiently managing user access end-to-end. Together, these make up the core pillars of a robust IAM program.
The Phases of Identity Lifecycle Management
The three main phases of Identity Lifecycle Management include:
- Onboarding and Provisioning: The initial stage involves creating a digital identity for new users and granting appropriate access to systems and data necessary for their roles.
- Managing Access Rights and Permissions: This phase focuses on adjusting user access rights as their roles change within the organization, ensuring they have the necessary permissions to perform their job functions while maintaining security compliance.
- Offboarding and De-Provisioning: The final stage covers removing access rights and securely deactivating or deleting the digital identity once it is no longer needed, such as when an employee leaves the company.
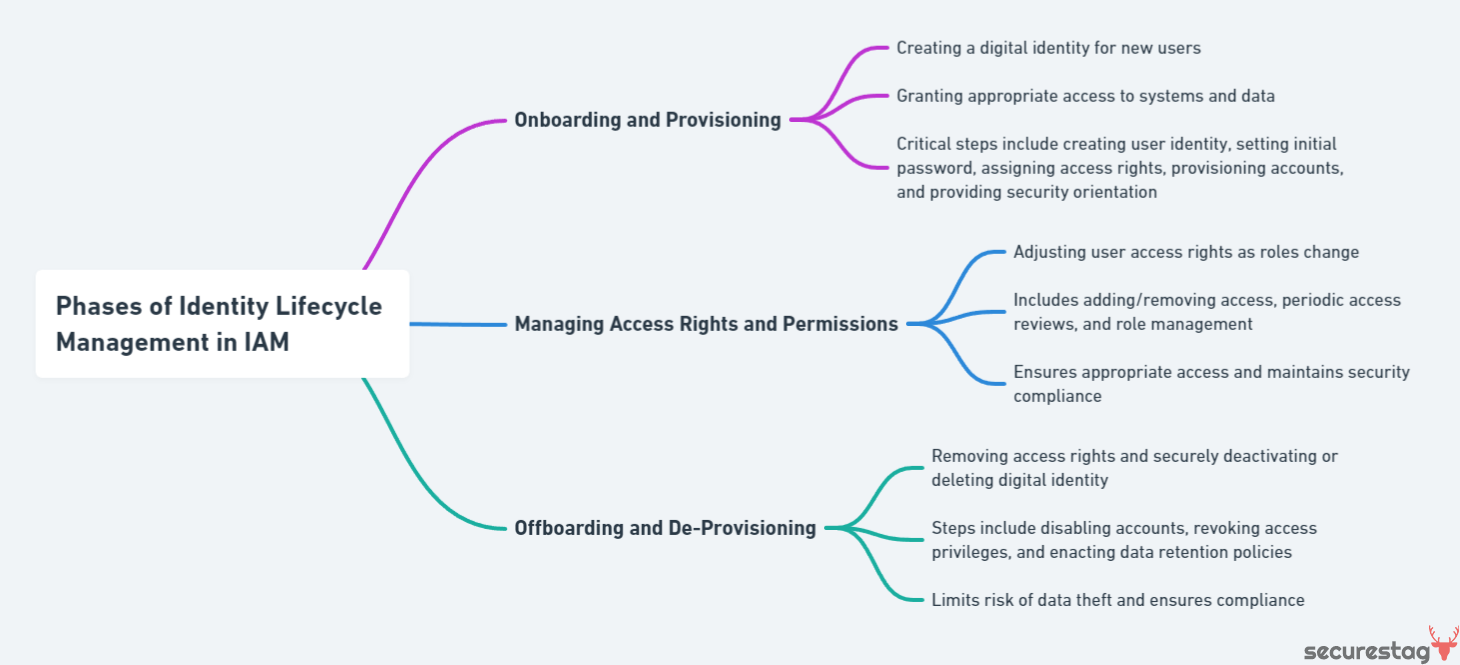
These phases work together to streamline the management of digital identities, strengthen security, and support compliance with relevant regulations.
Onboarding and Provisioning: The First Steps in Identity Management
Onboarding and provisioning are the initial phases of the identity lifecycle when a new user joins an organization. They involve creating a new user identity and setting initial access rights to systems and data.
According to onboarding statistics, up to 20% of staff turnover happens within the first 45 days of employment. This highlights the importance of a smooth onboarding process in retaining new hires. Proper onboarding and provisioning ensures new employees have the access they need on day one to be productive.
Some critical steps in onboarding and provisioning include:
- Creating a user identity in the organization’s directory with details like name, department, job title, etc.
- Setting an initial password or sending a temporary password for the first login.
- Assigning access rights and permissions based on the user’s role. This controls what resources they can access.
- Provisioning accounts in all necessary target systems like Active Directory, Entra ID (Azure AD), Microsoft Exchange, collaboration tools, databases, etc.
- Providing orientation on security policies and proper access procedures.
According to Brandon Hall Group, only 37% of companies extend their onboarding process beyond 30 days. However, effective onboarding is not a one-time event; it should be an ongoing process as the employee settles into their new role. Proper access rights and permissions also need to be maintained over time.
Managing Access Rights and Permissions
Managing user access rights and permissions is critical to identity lifecycle management. Organizations must have processes to grant the appropriate access rights when users join, modify access while users are active, and revoke all access when users leave the organization. Critical components of managing access rights include:
- Adding/removing access: When a new employee joins, access must be provisioned to the appropriate resources based on their role. When an employee’s role changes, access should be modified to align with the new responsibilities. Upon termination, all access must be revoked immediately.
- Periodic access reviews: Organizations should conduct periodic access reviews or recertifications to evaluate whether users still require the same level of access. This helps eliminate unused, excessive, or improper permissions.
- Role management: Rather than handling access individually, access rights and permissions should be grouped into roles corresponding to job functions. As employees enter and leave roles, their access adjusts automatically.
Properly managing access rights is crucial for maintaining security and compliance. Failing to remove permissions when employees depart creates the risk of data theft or unauthorized access. Regular reviews help organizations follow the principle of least privilege. Automating access management through role-based models improves efficiency. Overall, strong access governance ensures organizations only grant access that meets business needs while minimizing risk.
Offboarding and De-Provisioning: Ensuring a Secure Departure
A critical phase of identity lifecycle management is ensuring proper offboarding and de-provisioning when employees leave the organization. This involves disabling accounts, revoking access rights across all systems and platforms, and enacting data retention policies.
Disabling accounts is the first step when offboarding employees. This prevents former employees from logging into systems and accessing data. Best practices recommend disabling accounts immediately upon termination or resignation. Leaving accounts active, even for a few hours, poses security risks.
The next priority is revoking access privileges across all applications, networks, and systems. Former employees should not retain any access rights post-departure. Integrations across IAM systems and HR can help automate this process.
Finally, data retention policies should address what happens to an ex-employee’s files and information. While some data may need to be accessible for compliance or legal reasons, most should be permanently deleted after a set period. This reduces security exposure and storage costs.
Proper offboarding limits the risk of data theft and malicious insider attacks by former employees. It also ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR.
Best Practices for Effective Identity Lifecycle Management
Implementing best practices for effective Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM) is essential for enhancing security, compliance, and operational efficiency in Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems. These practices ensure that digital identities are managed securely and efficiently throughout their lifecycle within an organization. Essential best practices include:
- Automating Identity Management Processes: Utilizing automation tools for onboarding, provisioning, managing access rights, and offboarding to reduce manual errors, save time, and ensure consistency across the identity management process.
- Continuous Monitoring and Review of Access Rights: Implement regular audits and reviews of user access rights to detect inappropriate permissions or access creep and ensure that users have only the access necessary for their current roles.
- Integrating IAM with Other Security Solutions: Linking IAM systems with other security technologies like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), privileged access management (PAM), and multi-factor authentication tools to create a layered security infrastructure that can respond dynamically to evolving threats.
Sticking to these best practices helps organizations maintain a secure and compliant IAM framework that supports business processes and protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Challenges in Implementing Identity Lifecycle Management
Implementing Identity Lifecycle Management within IAM frameworks presents its unique challenges, which are critical to address for the success of IAM initiatives. Navigating these challenges requires a thoughtful approach, leveraging technology and best practices to achieve a secure, compliant, and user-friendly IAM ecosystem.
Balancing Security with User Convenience
Balancing security with user convenience in the IAM (Identity and Access Management) domain is crucial for maintaining efficient operations and ensuring robust security. This delicate balance demands strategies that safeguard assets and facilitate a frictionless user experience. Notably:
- Organizations face the challenge of integrating advanced authentication methods that are user-friendly yet provide strong security. Leveraging technologies like Single Sign-On (SSO) simplifies access by using a single set of credentials for multiple applications, enhancing both user convenience and security.
- Implementing self-service password management reduces dependency on IT support for password resets, empowering users to manage their credentials independently. Thus, users can streamline their experience without compromising security.
- Passwordless authentication methods, such as biometrics or security keys, offer a secure and seamless alternative to traditional passwords. They significantly enhance the user experience by eliminating common pain points associated with password management.
- Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) tailors security requirements based on the context of each login attempt, adjusting the authentication process dynamically to balance security needs with user convenience.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Most enterprises today operate under some form of regulatory compliance mandates that apply to how they manage and secure user access and data. Some of the most common regulations that impact identity lifecycle management processes include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR imposes regulations around securing and managing the personal data of EU residents. Effective ILM is crucial for meeting requirements like data minimization, consent management, and the right to erasure.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): SOX sets standards for internal controls and auditing processes, mandating that companies maintain adequate controls over financial reporting data and systems. IAM solutions help meet SOX controls around access management and segregation of duties.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): For healthcare organizations in the US, HIPAA establishes security safeguards around patient health information. ILM capabilities like access reviews and de-provisioning support HIPAA compliance by securing ePHI data. Effective identity lifecycle management is crucial for simplifying compliance processes and passing audits through capabilities like automated user provisioning/de-provisioning, access reviews and recertifications, and role-based access controls. Companies need reporting tools to demonstrate compliance with required controls and standards. Integrating ILM processes with GRC platforms provides a holistic view of compliance status across the identity environment.
Addressing the Complexity of Hybrid IT Environments
Identity lifecycle management can become quite complex as organizations adopt hybrid IT environments comprising both on-premises and cloud infrastructure. This introduces several key challenges:
- Managing identities and access across on-prem, hybrid, and cloud systems.
- Providing integrated IAM capabilities span on-prem directories like Active Directory and modern cloud apps and platforms.
- Managing external users outside the corporate network, such as customers, partners, third parties, B2B, and remote employees. These users still need access to specific resources, so their identities and access rights must be incorporated into ILM programs.
- Keeping up with growing complexity as IT environments expand to incorporate more applications, platforms, devices, and integration touchpoints. Each new component further challenges connecting disparate identity stores and streamlining ILM workflows.
Implementing robust identity lifecycle management across today’s complex hybrid IT environments remains a key struggle for many organizations. It requires thinking beyond the technology to the governance, processes, and integration needed to drive security and efficiency.
Future Trends in Identity Lifecycle Management
Identity and access management (IAM) rapidly evolves to meet new security and efficiency demands. Several key trends are emerging that will shape the future of identity lifecycle management (ILM):
The Role of AI and ML in Enhancing IAM
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being applied to IAM to automate processes and enhance security. ML algorithms can detect anomalous behavior and spot potential threats. AI virtual assistants can handle everyday IAM tasks to improve efficiency. Intelligent identity analytics provide deeper visibility into users and entitlements. As AI/ML capabilities grow, they will become integral to ILM.
Moving Towards a Zero Trust Security Model
Organizations are increasingly adopting a Zero Trust approach in their IAM strategy. This model assumes no implicit trust and continuously validates every user transaction. Advanced MFA, user behavior analytics, and microsegmentation help enforce least privilege access under zero trust, providing tighter access controls across the identity lifecycle.
The Importance of Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
IDaaS solutions are becoming more popular for streamlining ILM. IDaaS provides cloud-based identity management delivered as a service. It enables seamless integration across cloud apps and systems. IDaaS offerings incorporate automation, analytics, and AI to simplify ILM. As hybrid environments spread, IDaaS can unify IAM across on-prem and cloud.
Conclusion: Maximizing Security and Efficiency with ILM
In the journey through Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM), we’ve explored the critical phases from onboarding to offboarding, highlighted the best practices that ensure a robust yet user-friendly environment, and navigated the challenges that complicate ILM implementation. The future of ILM promises further innovations that will continue to shape the security landscape, addressing emerging threats and embracing new technologies.
To effectively manage digital identities, organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to ILM, including implementing current best practices and staying ahead of future trends by embracing innovative solutions that enhance security without sacrificing user convenience. Integrating ILM into the broader IAM strategy is crucial for creating a more secure and efficient digital environment.
We at SecureStag believe that improving the security posture through ILM is a continuous journey that reflects the dynamic nature of technology and cyber threats. Organizations that commit to this ongoing process by leveraging automation, adopting adaptive authentication methods, and integrating advanced security solutions will be well-positioned to protect their assets and users in the digital age.


